What Best Describes the Role of Dna in the Body
Best For Family Trees Ancestry Research. It plays a key role in breaking down homocysteine an amino acid that can exert harmful effects in the body if it is present in high amounts.
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Magnesium also plays a role in the active transport of calcium and potassium ions across cell membranes a process that is important to nerve impulse conduction muscle contraction and normal heart rhythm.

. The role of mRNA is to carry protein information from the DNA in a cells nucleus to the cells cytoplasm watery interior where the protein-making machinery reads the mRNA sequence and translates each three-base codon into its corresponding amino acid in a growing protein chain. As a normal cellular process a small portion of telomeric DNA is lost with each cell division. Explore the types of proteins and learn about their varied functions.
Folate helps to form DNA and RNA and is involved in protein metabolism. However even the darkest skin type incurred significant DNA damage at levels less than or equal to 1 MED underscoring the. The observations made in these studies allow the conclusions that DNA damage is greatest immediately after UV exposure and is gradually repaired thereafter and that subjects with darker skin type incur less DNA damage than subjects with lighter skin.
As their name suggests AncestryDNA a subsidiary of the larger company Ancestry primarily offers ancestry information in the form of ethnicity estimates as well as a family DNA. DNA analysis can help build the family tree. Transcribe and Translate a Gene.
Messenger RNA or mRNA. Find out about autosomal x chromosome y chromosome and mitochondrial DNA. The coming years will usher in a number of body augmentation capabilities that will enable humans to be smarter stronger and more capable than we are today.
Telomeres therefore play a vital role in preserving the information in our genome. So mRNA really is a form of nucleic acid. This article describes the normal role of thiamine in brain functioning as well as the pathological consequences that result from thiamine deficiency.
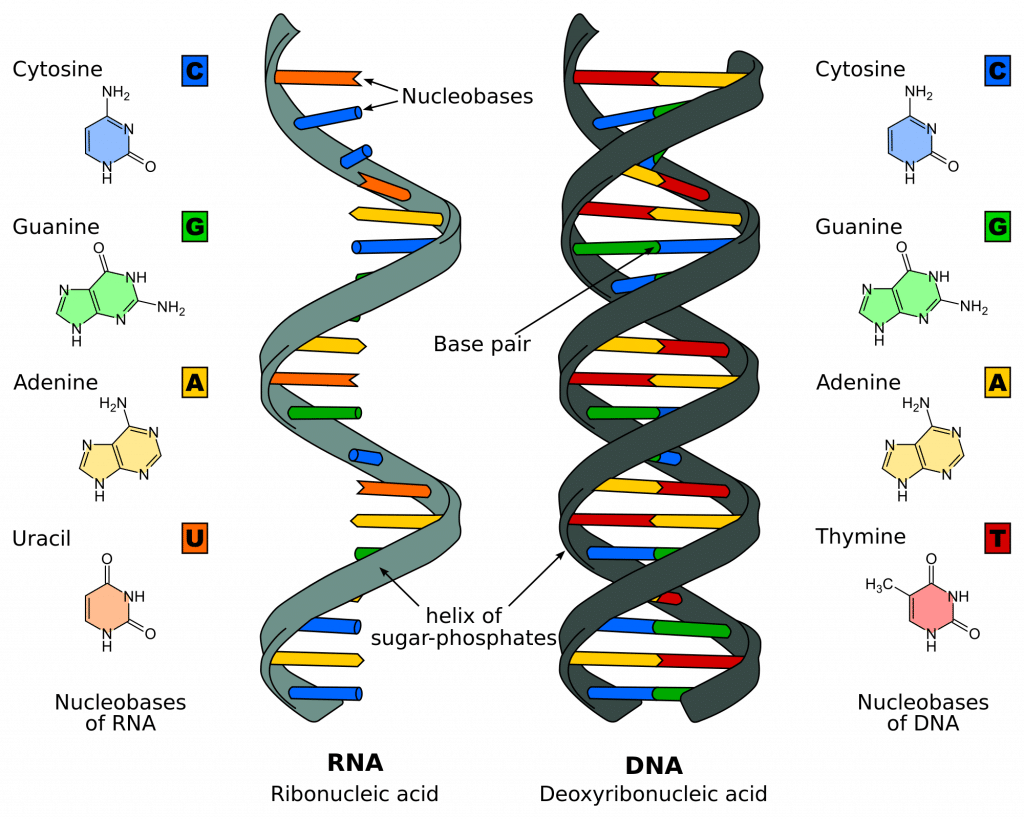
DNA exists as a double-stranded structure with both strands coiled together to form the characteristic double-helixEach single strand of DNA is a chain of four types of nucleotidesNucleotides in DNA contain a deoxyribose sugar a phosphate and a nucleobaseThe four types of nucleotide correspond to the four nucleobases adenine cytosine guanine and. Wearables will be one form of body. Specific actions of thiamine on a cellular level then are reviewed followed by a discussion of how alcohol affects the bodys processing and availability of thiamine as well as thiamine utilization by the cells.
An adult body contains approximately 25 g magnesium with 50 to 60 present in the bones and most of the rest in soft tissues. Finally the article explores. See how cells read the information in a DNA sequence to.
Folate is also needed to produce healthy red blood cells and is critical during periods of rapid growth such as during pregnancy and fetal development. Telomeres the specific DNAprotein structures found at both ends of each chromosome protect genome from nucleolytic degradation unnecessary recombination repair and interchromosomal fusion. With over 15 million completed DNA samples AncestryDNA boasts the worlds largest commercial genetic genealogy database.

Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology

Comments
Post a Comment